Hash function
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
(Redirected from
Hash code)
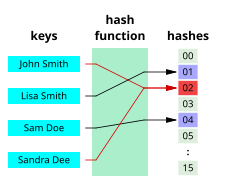
A hash function that maps names to integers from 0 to 15. There is a collision between keys "John Smith" and "Sandra Dee".
A
hash function is any
algorithm or
subroutine that maps large
data sets of variable length, called
keys, to smaller data sets of a fixed length. For example, a person's name, having a variable length, could be hashed to a single
integer. The values returned by a hash function are called
hash values,
hash codes,
hash sums,
checksums or simply
hashes.
Descriptions
Hash functions are mostly used to accelerate table lookup or data comparison tasks such as finding items in a
database, detecting duplicated or similar
records in a large
file, finding similar stretches in
DNA sequences, and so on.
A hash function should be
referentially transparent
(stable), i.e., if called twice on input that is "equal" (for example,
strings that consist of the same sequence of characters), it should give
the same result. This is a contract in many programming languages that
allow the user to override equality and hash functions for an object: if
two objects are equal, their hash codes must be the same. This is
crucial to finding an element in a hash table quickly, because two of
the same element would both hash to the same slot.
Some hash functions may map two or more keys to the same hash value, causing a
collision.
Such hash functions try to map the keys to the hash values as evenly as
possible because collisions become more frequent as hash tables fill
up. Thus, single-digit hash values are frequently restricted to 80% of
the size of the table. Depending on the algorithm used, other properties
may be required as well, such as
double hashing and
linear probing. Although the idea was conceived in the 1950s,
[1] the design of good hash functions is still a topic of active research.
Hash functions are related to (and often confused with)
checksums,
check digits,
fingerprints,
randomization functions,
error correcting codes, and
cryptographic hash functions.
Although these concepts overlap to some extent, each has its own uses
and requirements and is designed and optimized differently. The
HashKeeper database maintained by the American
National Drug Intelligence Center, for instance, is more aptly described as a catalog of file fingerprints than of hash values.
Hash tables
Hash functions are primarily used in
hash tables, to quickly locate a data record (for example, a
dictionary definition) given its
search key
(the headword). Specifically, the hash function is used to map the
search key to the hash. The index gives the place where the
corresponding record should be stored. Hash tables, in turn, are used to
implement
associative arrays and
dynamic sets.
In general, a hashing function may map several different keys to the
same index. Therefore, each slot of a hash table is associated with
(implicitly or explicitly) a
set of records, rather than a single record. For this reason, each slot of a hash table is often called a
bucket, and hash values are also called
bucket indices.
Thus, the hash function only hints at the record's location—it tells
where one should start looking for it. Still, in a half-full table, a
good hash function will typically narrow the search down to only one or
two entries.
Caches
Hash functions are also used to build
caches
for large data sets stored in slow media. A cache is generally simpler
than a hashed search table, since any collision can be resolved by
discarding or writing back the older of the two colliding items. This is
also used in file comparison.
Bloom filters
Main article:
Bloom filter
Hash functions are an essential ingredient of the
Bloom filter, a compact data structure that provides an enclosing approximation to a set of them.
[2]
Finding duplicate records
When storing records in a large unsorted file, one may use a hash function to map each record to an index into a table
T, and collect in each bucket
T[
i] a
list of the numbers of all records with the same hash value
i.
Once the table is complete, any two duplicate records will end up in
the same bucket. The duplicates can then be found by scanning every
bucket
T[
i] which contains two or more members, fetching
those records, and comparing them. With a table of appropriate size,
this method is likely to be much faster than any alternative approach
(such as sorting the file and comparing all consecutive pairs).
Finding similar records
Hash functions can also be used to locate table records whose key is
similar, but not identical, to a given key; or pairs of records in a
large file which have similar keys. For that purpose, one needs a hash
function that maps similar keys to hash values that differ by at most
m, where
m is a small integer (say, 1 or 2). If one builds a table
T
of all record numbers, using such a hash function, then similar records
will end up in the same bucket, or in nearby buckets. Then one need
only check the records in each bucket
T[
i] against those in buckets
T[
i+
k] where
k ranges between −
m and
m.
This class includes the so-called
acoustic fingerprint algorithms, that are used to locate similar-sounding entries in large collection of
audio files.
For this application, the hash function must be as insensitive as
possible to data capture or transmission errors, and to "trivial"
changes such as timing and volume changes, compression, etc.
[3]
Finding similar substrings
The same techniques can be used to find equal or similar stretches in
a large collection of strings, such as a document repository or a
genomic database.
In this case, the input strings are broken into many small pieces, and a
hash function is used to detect potentially equal pieces, as above.
The
Rabin–Karp algorithm is a relatively fast
string searching algorithm that works in
O(n) time on average. It is based on the use of hashing to compare strings.
Geometric hashing
This principle is widely used in
computer graphics,
computational geometry and many other disciplines, to solve many
proximity problems in the plane or in three-dimensional space, such as finding
closest pairs in a set of points, similar shapes in a list of shapes, similar
images in an
image database, and so on. In these applications, the set of all inputs is some sort of
metric space, and the hashing function can be interpreted as a
partition of that space into a grid of
cells. The table is often an array with two or more indices (called a
grid file,
grid index,
bucket grid, and similar names), and the hash function returns an index
tuple. This special case of hashing is known as
geometric hashing or
the grid method. Geometric hashing is also used in
telecommunications (usually under the name
vector quantization) to
encode and
compress multi-dimensional signals.
Properties
Good hash functions, in the original sense of the term, are usually
required to satisfy certain properties listed below. Note that different
requirements apply to the other related concepts (
cryptographic hash functions, checksums, etc.).
Determinism
A hash procedure must be
deterministic—meaning that for a given input value it must always generate the same hash value. In other words, it must be a
function
of the data to be hashed, in the mathematical sense of the term. This
requirement excludes hash functions that depend on external variable
parameters, such as
pseudo-random number generators
or the time of day. It also excludes functions that depend on the
memory address of the object being hashed, because that address may
change during execution (as may happen on systems that use certain
methods of
garbage collection), although sometimes rehashing of the item is possible.
Uniformity
A good hash function should map the expected inputs as evenly as
possible over its output range. That is, every hash value in the output
range should be generated with roughly the same
probability. The reason for this last requirement is that the cost of hashing-based methods goes up sharply as the number of
collisions—pairs
of inputs that are mapped to the same hash value—increases. Basically,
if some hash values are more likely to occur than others, a larger
fraction of the lookup operations will have to search through a larger
set of colliding table entries.
Note that this criterion only requires the value to be
uniformly distributed, not
random
in any sense. A good randomizing function is (barring computational
efficiency concerns) generally a good choice as a hash function, but the
converse need not be true.
Hash tables often contain only a small subset of the valid inputs.
For instance, a club membership list may contain only a hundred or so
member names, out of the very large set of all possible names. In these
cases, the uniformity criterion should hold for almost all typical
subsets of entries that may be found in the table, not just for the
global set of all possible entries.
In other words, if a typical set of
m records is hashed to
n table slots, the probability of a bucket receiving many more than
m/
n records should be vanishingly small. In particular, if
m is less than
n, very few buckets should have more than one or two records. (In an ideal "
perfect hash function", no bucket should have more than one record; but a small number of collisions is virtually inevitable, even if
n is much larger than
m – see the
birthday paradox).
When testing a hash function, the uniformity of the distribution of hash values can be evaluated by the
chi-squared test.
Variable range
In many applications, the range of hash values may be different for
each run of the program, or may change along the same run (for instance,
when a hash table needs to be expanded). In those situations, one needs
a hash function which takes two parameters—the input data
z, and the number
n of allowed hash values.
A common solution is to compute a fixed hash function with a very large range (say, 0 to 2
32 − 1), divide the result by
n, and use the division's
remainder. If
n is itself a power of 2, this can be done by
bit masking and
bit shifting. When this approach is used, the hash function must be chosen so that the result has fairly uniform distribution between 0 and
n − 1, for any value of
n that may occur in the application. Depending on the function, the remainder may be uniform only for certain values of
n, e.g.
odd or
prime numbers.
We can allow the table size
n to not be a power of 2 and still
not have to perform any remainder or division operation, as these
computations are sometimes costly. For example, let
n be significantly less than 2
b. Consider a pseudo random number generator (
PRNG) function
P(key) that is uniform on the interval [0, 2
b − 1]. A hash function uniform on the interval [0, n-1] is
n P(key)/2
b. We can replace the division by a (possibly faster) right
bit shift:
nP(key) >>
b.
Variable range with minimal movement (dynamic hash function)
When the hash function is used to store values in a hash table that
outlives the run of the program, and the hash table needs to be expanded
or shrunk, the hash table is referred to as a dynamic hash table.
A hash function that will relocate the minimum number of records when
the table is resized is desirable. What is needed is a hash function
H(
z,
n) – where
z is the key being hashed and
n is the number of allowed hash values – such that
H(
z,
n + 1) =
H(
z,
n) with probability close to
n/(
n + 1).
Linear hashing
and spiral storage are examples of dynamic hash functions that execute
in constant time but relax the property of uniformity to achieve the
minimal movement property.
Extendible hashing uses a dynamic hash function that requires space proportional to
n to compute the hash function, and it becomes a function of the previous keys that have been inserted.
Several algorithms that preserve the uniformity property but require time proportional to
n to compute the value of
H(
z,
n) have been invented.
Data normalization
In some applications, the input data may contain features that are
irrelevant for comparison purposes. For example, when looking up a
personal name, it may be desirable to ignore the distinction between
upper and lower case letters. For such data, one must use a hash
function that is compatible with the data
equivalence
criterion being used: that is, any two inputs that are considered
equivalent must yield the same hash value. This can be accomplished by
normalizing the input before hashing it, as by upper-casing all letters.
Continuity
A hash function that is used to search for similar (as opposed to equivalent) data must be as
continuous as possible; two inputs that differ by a little should be mapped to equal or nearly equal hash values.
[citation needed]
Note that continuity is usually considered a fatal flaw for checksums,
cryptographic hash functions,
and other related concepts. Continuity is desirable for hash functions
only in some applications, such as hash tables that use
linear search.
Hash function algorithms
For most types of hashing functions the choice of the function depends strongly on the nature of the input data, and their
probability distribution in the intended application.
Trivial hash function
If the datum to be hashed is small enough, one can use the datum
itself (reinterpreted as an integer in binary notation) as the hashed
value. The cost of computing this "trivial" (
identity) hash function is effectively zero. This hash function is
perfect, as it maps each input to a distinct hash value.
The meaning of "small enough" depends on the size of the type that is used as the hashed value. For example, in
Java, the hash code is a 32-bit integer. Thus the 32-bit integer
Integer and 32-bit floating-point
Float objects can simply use the value directly; whereas the 64-bit integer
Long and 64-bit floating-point
Double cannot use this method.
Other types of data can also use this perfect hashing scheme. For example, when mapping
character strings between
upper and lower case,
one can use the binary encoding of each character, interpreted as an
integer, to index a table that gives the alternative form of that
character ("A" for "a", "8" for "8", etc.). If each character is stored
in 8 bits (as in
ASCII or
ISO Latin 1), the table has only 2
8 = 256 entries; in the case of
Unicode characters, the table would have 17×2
16 = 1114112 entries.
The same technique can be used to map
two-letter country codes like "us" or "za" to country names (26
2=676
table entries), 5-digit zip codes like 13083 to city names (100000
entries), etc. Invalid data values (such as the country code "xx" or the
zip code 00000) may be left undefined in the table, or mapped to some
appropriate "null" value.
Perfect hashing

A perfect hash function for the four names shown
A hash function that is
injective—that is, maps each valid input to a different hash value—is said to be
perfect. With such a function one can directly locate the desired entry in a hash table, without any additional searching.
Minimal perfect hashing

A minimal perfect hash function for the four names shown
A perfect hash function for
n keys is said to be
minimal if its range consists of
n consecutive integers, usually from 0 to
n−1.
Besides providing single-step lookup, a minimal perfect hash function
also yields a compact hash table, without any vacant slots. Minimal
perfect hash functions are much harder to find than perfect ones with a
wider range.
Hashing uniformly distributed data
If the inputs are bounded-length
strings (such as
telephone numbers,
car license plates,
invoice numbers, etc.), and each input may
independently occur with
uniform
probability, then a hash function need only map roughly the same number
of inputs to each hash value. For instance, suppose that each input is
an integer
z in the range 0 to
N−1, and the output must be an integer
h in the range 0 to
n−1, where
N is much larger than
n. Then the hash function could be
h =
z mod n (the remainder of
z divided by
n), or
h = (
z ×
n) ÷
N (the value
z scaled down by
n/
N and truncated to an integer), or many other formulas.
Warning:
h =
z mod n was used in many of the original random number generators, but was found to have a number of issues. One of which is that as
n approaches
N, this function becomes less and less uniform.
Hashing data with other distributions
These simple formulas will not do if the input values are not equally
likely, or are not independent. For instance, most patrons of a
supermarket
will live in the same geographic area, so their telephone numbers are
likely to begin with the same 3 to 4 digits. In that case, if
m is 10000 or so, the division formula (
z ×
m) ÷
M, which depends mainly on the leading digits, will generate a lot of collisions; whereas the remainder formula
z mod M, which is quite sensitive to the trailing digits, may still yield a fairly even distribution.
Hashing variable-length data
When the data values are long (or variable-length)
character strings—such as personal names,
web page addresses, or mail messages—their distribution is usually very uneven, with complicated dependencies. For example, text in any
natural language has highly non-uniform distributions of
characters, and
character pairs,
very characteristic of the language. For such data, it is prudent to
use a hash function that depends on all characters of the string—and
depends on each character in a different way.
In cryptographic hash functions, a
Merkle–Damgård construction is usually used. In general, the scheme for hashing such data is to break the input into a sequence of small units (
bits,
bytes,
words, etc.) and combine all the units
b[1],
b[2], ...,
b[
m] sequentially, as follows
S ← S0; // Initialize the state.
for k in 1, 2, ..., m do // Scan the input data units:
S ← F(S, b[k]); // Combine data unit k into the state.
return G(S, n) // Extract the hash value from the state.
This schema is also used in many text checksum and fingerprint algorithms. The state variable
S may be a 32- or 64-bit unsigned integer; in that case,
S0 can be 0, and
G(
S,
n) can be just
S mod n. The best choice of
F is a complex issue and depends on the nature of the data. If the units
b[
k] are single bits, then
F(
S,
b) could be, for instance
if highbit(S) = 0 then
return 2 * S + b
else
return (2 * S + b) ^ P
Here
highbit(
S) denotes the most significant bit of
S; the '
*' operator denotes unsigned integer multiplication with lost
overflow; '
^' is the bitwise
exclusive or operation applied to words; and
P is a suitable fixed word.
[4]
Special-purpose hash functions
In many cases, one can design a special-purpose (
heuristic)
hash function that yields many fewer collisions than a good
general-purpose hash function. For example, suppose that the input data
are file names such as
FILE0000.CHK,
FILE0001.CHK,
FILE0002.CHK, etc., with mostly sequential numbers. For such data, a function that extracts the numeric part
k of the file name and returns
k mod n
would be nearly optimal. Needless to say, a function that is
exceptionally good for a specific kind of data may have dismal
performance on data with different distribution.
Rolling hash
Main article:
rolling hash
In some applications, such as
substring search, one must compute a hash function
h for every
k-character
substring of a given
n-character string
t; where
k is a fixed integer, and
n is
k. The straightforward solution, which is to extract every such substring
s of
t and compute
h(
s) separately, requires a number of operations proportional to
k·
n. However, with the proper choice of
h, one can use the technique of rolling hash to compute all those hashes with an effort proportional to
k +
n.
Universal hashing
A
universal hashing scheme is a
randomized algorithm that selects a hashing function
h among a family of such functions, in such a way that the probability of a collision of any two distinct keys is 1/
n, where
n
is the number of distinct hash values desired—independently of the two
keys. Universal hashing ensures (in a probabilistic sense) that the hash
function application will behave as well as if it were using a random
function, for any distribution of the input data. It will however have
more collisions than perfect hashing, and may require more operations
than a special-purpose hash function.
Hashing with checksum functions
One can adapt certain checksum or fingerprinting algorithms for use
as hash functions. Some of those algorithms will map arbitrary long
string data
z, with any typical real-world distribution—no matter
how non-uniform and dependent—to a 32-bit or 64-bit string, from which
one can extract a hash value in 0 through
n − 1.
This method may produce a sufficiently uniform distribution of hash values, as long as the hash range size
n is small compared to the range of the checksum or fingerprint function. However, some checksums fare poorly in the
avalanche test,
which may be a concern in some applications. In particular, the popular
CRC32 checksum provides only 16 bits (the higher half of the result)
that are usable for hashing
[citation needed].
Moreover, each bit of the input has a deterministic effect on each bit
of the CRC32, that is one can tell without looking at the rest of the
input, which bits of the output will flip if the input bit is flipped;
so care must be taken to use all 32 bits when computing the hash from
the checksum.
[5]
Hashing with cryptographic hash functions
Some
cryptographic hash functions, such as
SHA-1,
have even stronger uniformity guarantees than checksums or
fingerprints, and thus can provide very good general-purpose hashing
functions.
In ordinary applications, this advantage may be too small to offset their much higher cost.
[6]
However, this method can provide uniformly distributed hashes even when
the keys are chosen by a malicious agent. This feature may help to
protect services against
denial of service attacks.
Hashing By Nonlinear Table Lookup
Tables of random numbers (such as 256 random 32 bit integers) can
provide high-quality nonlinear functions to be used as hash functions or
for other purposes such as cryptography. The key to be hashed would be
split into 8-bit (one byte) parts and each part will be used as an index
for the nonlinear table. The table values will be added by arithmetic
or XOR addition to the hash output value. Because the table is just 1024
bytes in size, it will fit into the cache of modern microprocessors and
allow for very fast execution of the hashing algorithm. As the table
value is on average much longer than 8 bits, one bit of input will
affect nearly all output bits. This is different to multiplicative hash
functions where higher-value input bits do not affect lower-value output
bits.
This algorithm has proven to be very fast and of high quality for hashing purposes (especially hashing of integer number keys).
Efficient Hashing Of Strings
Modern microprocessors will allow for much faster processing, if
8-bit character Strings are not hashed by processing one character at a
time, but by interpreting the string as an array of 32 bit or 64 bit
integers and hashing/accumulating these "wide word" integer values by
means of arithmetic operations (e.g. multiplication by constant and
bit-shifting). The remaining characters of the string which are smaller
than the word length of the CPU must be handled differently (e.g. being
processed one character at a time).
This approach has proven to speed up hash code generation by a factor
of five or more on modern microprocessors of a word size of 64 bit.
A far better approach for converting strings to a numeric value that
avoids the problem with some strings having great similarity
("Aaaaaaaaaa" and "Aaaaaaaaab") is to use a
Cyclic redundancy check
(CRC) of the string to compute a 32- or 64-bit value. While it is
possible that two different strings will have the same CRC, the
likelihood is very small and only requires that one check the actual
string found to determine whether one has an exact match. The CRC
approach works for strings of any length. CRCs will differ radically for
strings such as "Aaaaaaaaaa" and "Aaaaaaaaab".
Origins of the term
The term "hash" comes by way of analogy with its non-technical
meaning, to "chop and mix". Indeed, typical hash functions, like the
mod
operation, "chop" the input domain into many sub-domains that get
"mixed" into the output range to improve the uniformity of the key
distribution.
Donald Knuth notes that
Hans Peter Luhn of
IBM appears to have been the first to use the concept, in a memo dated January 1953, and that
Robert Morris used the term in a survey paper in
CACM which elevated the term from technical jargon to formal terminology.
[1]
List of hash functions
See also
 Computer science portal
Computer science portal
References
- ^ a b Knuth, Donald (1973). The Art of Computer Programming, volume 3, Sorting and Searching. pp. 506–542.
- ^ Bloom, Burton (July 1970). "Space/time trade-offs in hash coding with allowable errors". Communications of the ACM Volume 13 (Issue 7). doi:10.1145/362686.362692.
- ^ "Robust Audio Hashing for Content Identification by Jaap Haitsma, Ton Kalker and Job Oostveen"
- ^ Broder, A. Z. (1993). "Some applications of Rabin's fingerprinting method". Sequences II: Methods in Communications, Security, and Computer Science. Springer-Verlag. pp. 143–152.
- ^ Bret Mulvey, Evaluation of CRC32 for Hash Tables, in Hash Functions. Accessed April 10, 2009.
- ^ Bret Mulvey, Evaluation of SHA-1 for Hash Tables, in Hash Functions. Accessed April 10, 2009.
- ^ "Hash Functions". cse.yorku.ca. September 22, 2003. Retrieved November 1, 2012. "the djb2 algorithm (k=33) was first reported by dan bernstein many years ago in comp.lang.c."
External links






 တစ္ခု သတိျပဳေစခ်င္တာက ဒီလင့္ကေန Android apk ဖန္တီးလိုက္တဲ့အခါမွာ
မိမိရဲ့ Gmail ထဲသုိ႔ Auto သုိ႔မဟုတ္ Default apk ဖုိင္တစ္ခုကုိ
အရင္ဆုံးပုိ႔ေလ့ရွိပါတယ္။ ဒါေၾကာင့္ က်ေနာ္တုိ႔အေနနဲ႔ ေမးလ္ထဲမွာ AppYet (2) or (3) လို႔ ျဖစ္မွာသာ မိမိဖန္တီးလုိက္ေသာ application ရဲ့ Setting မ်ားအတုိင္းရရွိမွာ ျဖစ္ပါတယ္။
တစ္ခု သတိျပဳေစခ်င္တာက ဒီလင့္ကေန Android apk ဖန္တီးလိုက္တဲ့အခါမွာ
မိမိရဲ့ Gmail ထဲသုိ႔ Auto သုိ႔မဟုတ္ Default apk ဖုိင္တစ္ခုကုိ
အရင္ဆုံးပုိ႔ေလ့ရွိပါတယ္။ ဒါေၾကာင့္ က်ေနာ္တုိ႔အေနနဲ႔ ေမးလ္ထဲမွာ AppYet (2) or (3) လို႔ ျဖစ္မွာသာ မိမိဖန္တီးလုိက္ေသာ application ရဲ့ Setting မ်ားအတုိင္းရရွိမွာ ျဖစ္ပါတယ္။

 အားလုံး အဆင္ေျပပါေစ…
အားလုံး အဆင္ေျပပါေစ…














 ก่อนที่จะเปลี่ยนมือไปอยู่กับเจ้าของใหม่
เลยขอปล่อยรอมไว้เป็นที่ระลึกสักหนึ่งตัว Base rom ที่นำมาทำคือ
CyanogenMod 6 Rom 2.2 for Z71 ตัวที่เป็น RC ครับ
ก่อนที่จะเปลี่ยนมือไปอยู่กับเจ้าของใหม่
เลยขอปล่อยรอมไว้เป็นที่ระลึกสักหนึ่งตัว Base rom ที่นำมาทำคือ
CyanogenMod 6 Rom 2.2 for Z71 ตัวที่เป็น RC ครับ 






















